With plasma gasification, an electric arc heats a gas stream (air or nitrogen), at extremely elevated temperatures typically 50000C, thereby supplying the required energy to the process.
The plasma delivers energy needed to maintain the temperature inside the gasification reactor volume at values needed for dissociation of molecules of gases produced by material decomposition. Due to the elevated temperature the ash, metals and glass in the waste are melted, organic components are volatilized, and complex molecules are dissociated. 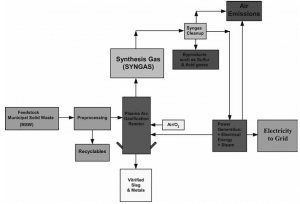 Molten slag is removed from the reactor, and after cooling and solidification, a substance similar to lava is produced. Organic materials, containing mostly chemically bound carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, are decomposed into syngas that can be utilised as various energy products, for example high quality fuel or electricity. Figure 1 is an illustration of the gasification process.
Molten slag is removed from the reactor, and after cooling and solidification, a substance similar to lava is produced. Organic materials, containing mostly chemically bound carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, are decomposed into syngas that can be utilised as various energy products, for example high quality fuel or electricity. Figure 1 is an illustration of the gasification process.






